이것은 인터랙티브 노트북입니다. 로컬에서 실행하거나 아래 링크를 사용할 수 있습니다: Weave와 OpenAI를 사용한 코드 생성
적절한 구조, 문서화 및 테스트가 포함된 고품질 코드를 생성하는 것은 어려운 작업입니다. 이 가이드는 코드 생성 파이프라인을 구현하는 방법을 보여줍니다. humaneval 테스트 스위트에 대해 고품질 Python 함수를 생성하는 코드 생성 파이프라인을 만드는 방법을 배우게 됩니다.
평가 비교 및 추적을 위해 Weave를 사용하고, 구조화된 출력을 통한 코드 생성을 위해 OpenAI의 GPT 모델을 사용할 것입니다.
비디오 시연
Weave, Groq 및 E2B를 사용한 코드 생성 파이프라인의 시각적 시연을 보려면 이 비디오를 확인하세요:
이 비디오는 Weave가 Groq와 통합되어 강력한 코드 생성 도구를 만드는 방법과 코드를 검증하기 위해 E2B에서 코드를 실행하는 과정을 단계별로 보여줍니다. 다음 예제에서는 OpenAI를 사용하지만, Weave와 함께 어떤 LLM 제공업체도 사용할 수 있습니다.
Weave를 사용하는 이유?
이 튜토리얼에서는 Weave를 사용하여 코드 생성 파이프라인을 구현하고 평가합니다. 다음과 같은 방법을 배우게 됩니다:
- LLM 파이프라인 추적: 코드 생성 프로세스의 입력, 출력 및 중간 단계를 기록합니다.
- LLM 출력 평가: 풍부한 디버깅 도구와 시각화를 통해 생성된 코드의 평가를 생성하고 비교합니다.
환경 설정
먼저, 환경을 설정하고 필요한 라이브러리를 가져오겠습니다:
!pip install -qU autopep8 autoflake weave isort openai set-env-colab-kaggle-dotenv datasets
python
%%capture
# Temporary workaround to fix bug in openai:
# TypeError: Client.__init__() got an unexpected keyword argument 'proxies'
# See https://community.openai.com/t/error-with-openai-1-56-0-client-init-got-an-unexpected-keyword-argument-proxies/1040332/15
!pip install "httpx<0.28"
python
import ast
import os
import re
import subprocess
import tempfile
import traceback
import autopep8
import isort
from autoflake import fix_code
from datasets import load_dataset
from openai import OpenAI
from pydantic import BaseModel
from set_env import set_env
import weave
from weave import Dataset, Evaluation
set_env("WANDB_API_KEY")
set_env("OPENAI_API_KEY")
python
WEAVE_PROJECT = "codegen-cookbook-example"
weave.init(WEAVE_PROJECT)
python
client = OpenAI()
python
human_eval = load_dataset("openai_humaneval")
selected_examples = human_eval["test"][:3]
Weave는 입력, 출력 및 메타데이터를 포함한 OpenAI API 호출을 자동으로 추적합니다. 이는 OpenAI 상호작용에 대한 추가 로깅 코드를 추가할 필요가 없다는 것을 의미합니다 - Weave가 백그라운드에서 원활하게 처리합니다.
구조화된 출력 및 Pydantic 모델 활용
이 코드 생성 파이프라인에서는 OpenAI의 structured outputs mode와 Pydantic 모델을 활용하여 언어 모델로부터 일관되고 잘 포맷된 응답을 보장합니다. 이 접근 방식은 여러 가지 장점을 제공합니다:
- 타입 안전성: Pydantic 모델을 사용하여 예상 출력을 정의함으로써, 생성된 코드, 프로그램 실행기 및 단위 테스트에 대한 엄격한 구조를 적용합니다.
- 쉬운 파싱: 구조화된 출력 모드를 사용하면 모델의 응답을 미리 정의된 Pydantic 모델로 직접 파싱할 수 있어, 복잡한 후처리 필요성이 줄어듭니다.
- 향상된 신뢰성: 우리가 기대하는 정확한 형식을 지정함으로써, 언어 모델로부터 예상치 못하거나 형식이 잘못된 출력이 나올 가능성을 줄입니다.
다음은 Pydantic 모델을 정의하고 OpenAI의 구조화된 출력과 함께 사용하는 방법의 예입니다:
class GeneratedCode(BaseModel):
function_signature: str
function_args_with_docstring_within_triple_quotes: str
code_logic: str
class FormattedGeneratedCode(BaseModel):
full_code: str
코드 포맷터 구현
일관되고 깔끔한 코드 출력을 보장하기 위해 CodeFormatter 클래스를 Weave 작업을 사용하여 구현합니다. 이 포맷터는 생성된 코드, 프로그램 실행기 및 단위 테스트에 다양한 린팅 및 스타일링 규칙을 적용합니다.
class CodeFormatter(BaseModel):
@weave.op()
def lint_code(self, code: str) -> str:
# Replace escaped newlines with actual newlines
code = code.replace("\\n", "\n")
# Remove unused imports and variables
code = fix_code(
code, remove_all_unused_imports=True, remove_unused_variables=True
)
# Sort imports
code = isort.code(code)
# Apply PEP 8 formatting
code = autopep8.fix_code(code, options={"aggressive": 2})
return code
@weave.op()
def add_imports(self, code: str) -> str:
tree = ast.parse(code)
from_imports = {}
global_names = set()
for node in ast.walk(tree):
if isinstance(node, ast.Name) and node.id not in dir(__builtins__):
global_names.add(node.id)
# Only add typing imports that are actually used
typing_imports = global_names.intersection(
{"List", "Dict", "Tuple", "Set", "Optional", "Union"}
)
if typing_imports:
from_imports["typing"] = typing_imports
# Remove names that are defined within the function
function_def = next(
node for node in tree.body if isinstance(node, ast.FunctionDef)
)
local_names = {arg.arg for arg in function_def.args.args}
local_names.update(
node.id
for node in ast.walk(function_def)
if isinstance(node, ast.Name) and isinstance(node.ctx, ast.Store)
)
global_names -= local_names
global_names -= {"sorted"} # Remove built-in functions
# Construct the import statements
import_statements = []
for module, names in from_imports.items():
names_str = ", ".join(sorted(names))
import_statements.append(f"from {module} import {names_str}")
return (
"\n".join(import_statements) + ("\n\n" if import_statements else "") + code
)
@weave.op()
def format_generated_code(
self, generated_code: GeneratedCode
) -> FormattedGeneratedCode:
# Combine the code parts
full_code = f"{generated_code.function_signature}\n{generated_code.function_args_with_docstring_within_triple_quotes}\n{generated_code.code_logic}"
# Ensure proper indentation
lines = full_code.split("\n")
indented_lines = []
for i, line in enumerate(lines):
if i == 0: # Function signature
indented_lines.append(line)
elif i == 1: # Function arguments (docstring)
indented_lines.append(" " + line)
else: # Function body
indented_lines.append(" " + line)
full_code = "\n".join(indented_lines)
# Lint the code
full_code = self.lint_code(full_code)
# Add imports
cleaned_code = self.add_imports(full_code)
return FormattedGeneratedCode(full_code=cleaned_code)
CodeFormatter 클래스는 생성된 코드를 정리하고 포맷팅하기 위한 여러 Weave 작업을 제공합니다:
- 이스케이프된 줄바꿈을 실제 줄바꿈으로 대체
- 사용되지 않는 임포트 및 변수 제거
- 임포트 정렬
- PEP 8 포맷팅 적용
- 누락된 임포트 추가
CodeGenerationPipeline 정의
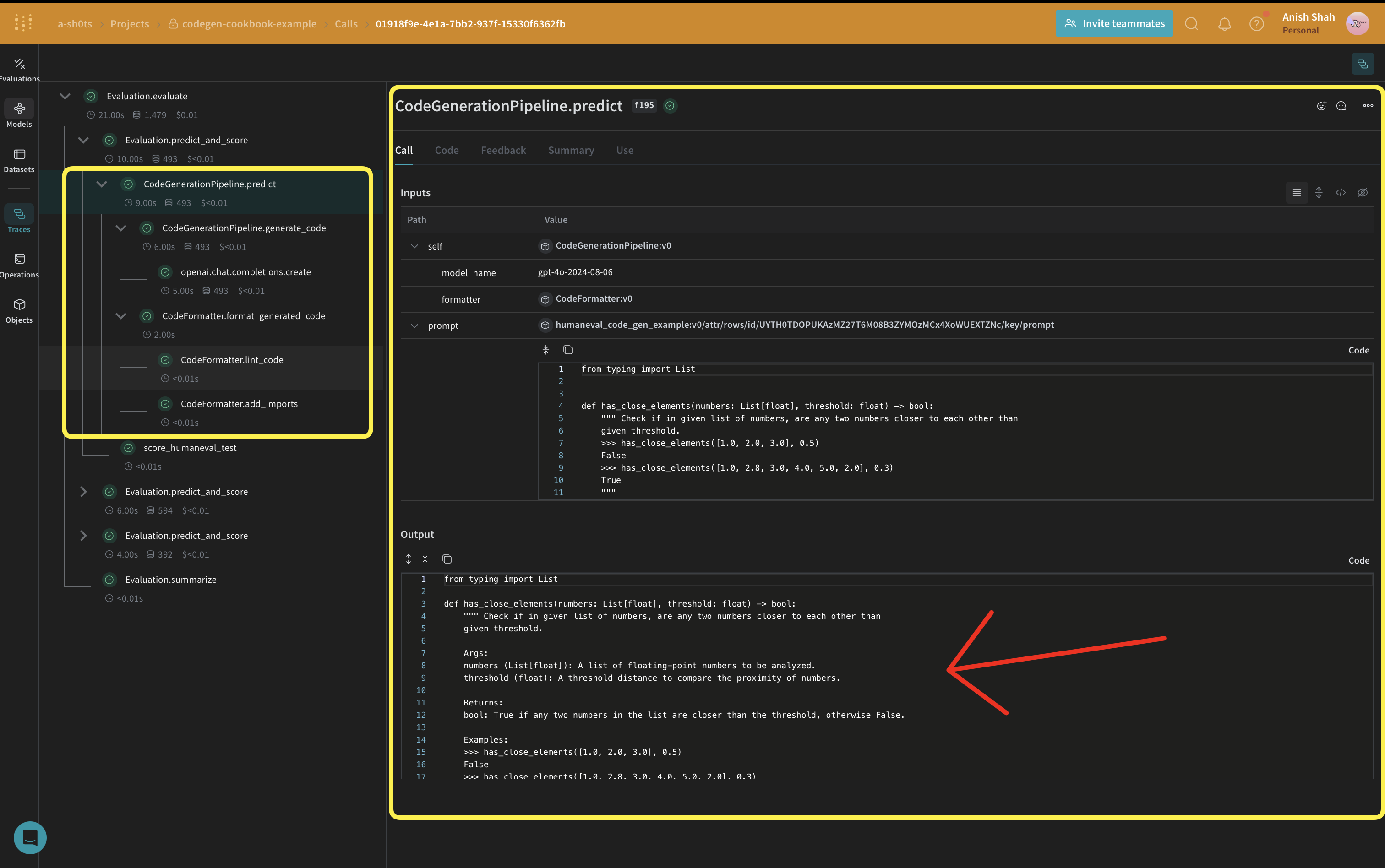 이제 핵심 코드 생성 로직을 구현해 보겠습니다:
우리는
이제 핵심 코드 생성 로직을 구현해 보겠습니다:
우리는 weave.Model를 사용하고 있어 변경될 때 자동으로 버전이 관리됩니다. 또한 model_name를 속성으로 유지하여 실험하고 Weave에서 쉽게 비교할 수 있습니다. 우리는 @weave.op로 함수 호출을 추적하여 입력 및 출력이 기록되어 오류 추적 및 디버깅에 도움이 됩니다.
class CodeGenerationPipeline(weave.Model):
model_name: str
formatter: CodeFormatter
def __init__(
self, model_name: str = "gpt-4o", formatter: CodeFormatter | None = None
):
if formatter is None:
formatter = CodeFormatter()
super().__init__(model_name=model_name, formatter=formatter)
self.model_name = model_name
self.formatter = formatter
@weave.op()
async def predict(self, prompt: str):
generated_code = self.generate_code(prompt)
formatted_generated_code = self.formatter.format_generated_code(generated_code)
return formatted_generated_code.full_code
@weave.op()
def generate_code(self, prompt: str) -> GeneratedCode:
completion = client.beta.chat.completions.parse(
model=self.model_name,
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are an expert Python code generator.",
},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
],
response_format=GeneratedCode,
)
message = completion.choices[0].message
if message.parsed:
return message.parsed
else:
raise ValueError(message.refusal)
CodeGenerationPipeline 클래스는 코드 생성 로직을 Weave Model로 캡슐화하여 여러 가지 주요 이점을 제공합니다:
- 자동 실험 추적: Weave는 모델의 각 실행에 대한 입력, 출력 및 매개변수를 캡처합니다.
- Versioning: Changes to the model’s attributes or code are automatically versioned, creating a clear history of how your code generation pipeline evolves over time.
- Reproducibility: The versioning and tracking make it easy to reproduce any previous result or configuration of your code generation pipeline.
- 하이퍼파라미터 관리: 모델 속성(예:
model_name)이 명확하게 정의되고 다양한 실행에서 추적되어 실험을 용이하게 합니다.
- Weave 생태계와의 통합:
weave.Model를 사용하면 평가 및 서빙 기능과 같은 다른 Weave 도구와 원활하게 통합됩니다.
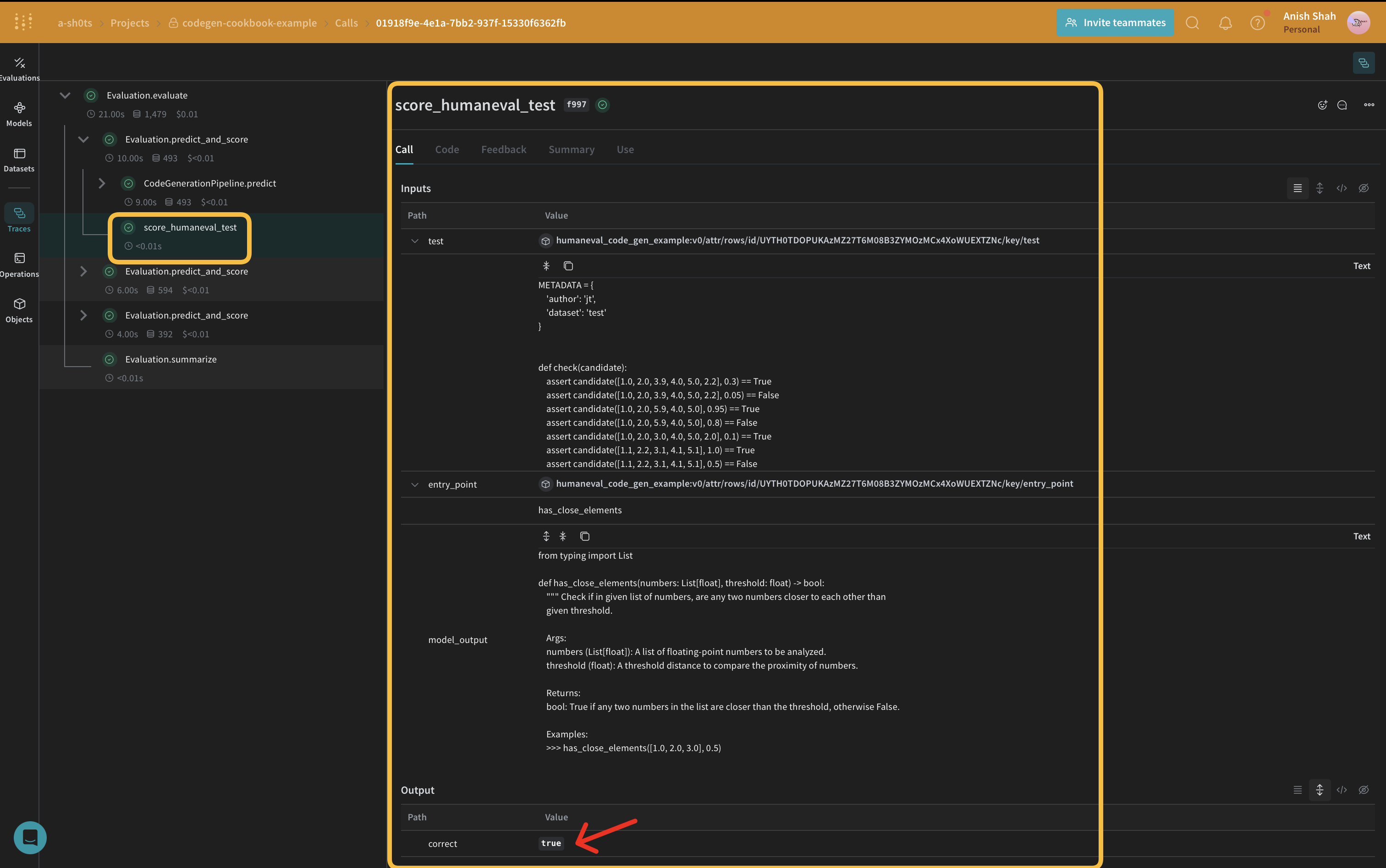
평가 지표 구현
생성된 코드의 품질을 평가하기 위해 weave.Scorer 서브클래스를 사용하여 간단한 평가 지표를 구현할 것입니다. 이는 데이터셋의 모든 score에 대해 model_output를 실행합니다. model_output는 predict 함수의 출력에서 가져옵니다 weave.Model. prompt는 데이터셋 human-eval에서 가져옵니다.
CODE_TEMPLATE = """
{model_output}
{test}
if __name__ == "__main__":
check({entry_point})
"""
python
@weave.op()
async def score_humaneval_test(test: str, entry_point: str, output: str):
generated_code = output
# Extract test cases from the test string
test_cases = re.findall(r"assert.*", test)
test_cases_str = "\n ".join(test_cases)
# Generate the full source code
full_code = CODE_TEMPLATE.format(
model_output=generated_code,
test=test,
test_cases=test_cases_str,
entry_point=entry_point,
)
# Create a temporary file to store the code
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(delete=False, suffix=".py") as tmp_file:
# Write the generated code to the temporary file
tmp_file.write(full_code.encode())
tmp_file_path = tmp_file.name
try:
# Run the temporary Python file as a subprocess with a timeout
result = subprocess.run(
["python", tmp_file_path],
capture_output=True,
text=True,
timeout=10, # Timeout of 10 seconds
)
print(result)
if result.returncode == 0:
return {"correct": True}
else:
return {"correct": False, "error": result.stderr, "output": result.stdout}
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
return {"correct": False, "error": "TimeoutExpired"}
except Exception as e:
return {"correct": False, "error": traceback.format_exc()}
finally:
# Ensure the temporary file is removed after execution
os.remove(tmp_file_path)
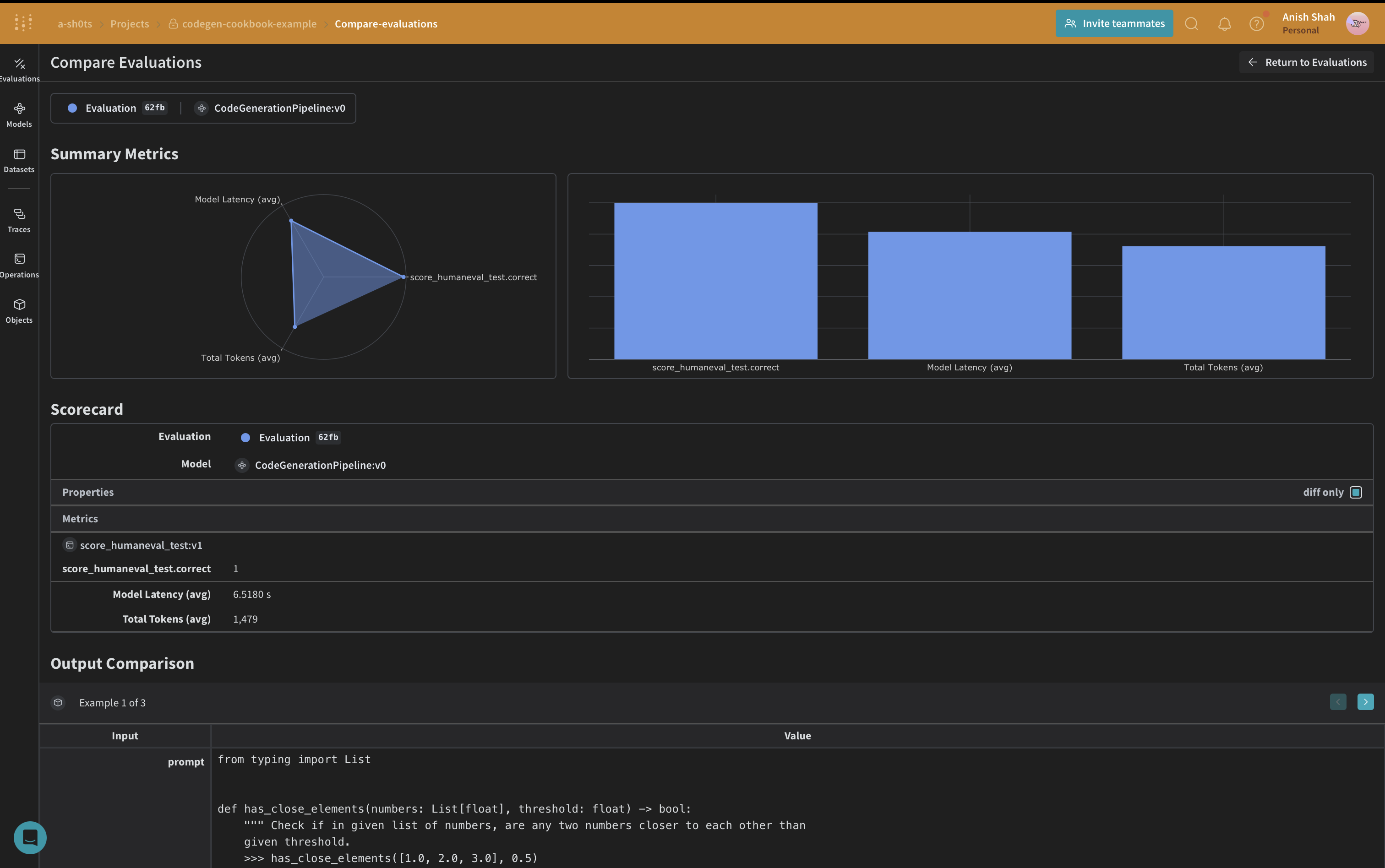
Weave 데이터셋 생성 및 평가 실행
파이프라인을 평가하기 위해 Weave 데이터셋을 생성하고 평가를 실행하겠습니다:
formatted_selected_examples = [
{
"task_id": task_id,
"prompt": prompt,
"canonical_solution": solution,
"test": test,
"entry_point": entry_point,
}
for task_id, prompt, solution, test, entry_point in zip(
selected_examples["task_id"],
selected_examples["prompt"],
selected_examples["canonical_solution"],
selected_examples["test"],
selected_examples["entry_point"],
)
]
python
prompt_dataset = Dataset(
name="humaneval_code_gen_example",
rows=[
{
"prompt": example["prompt"],
"test": example["test"],
"entry_point": example["entry_point"],
}
for example in formatted_selected_examples
],
)
weave.publish(prompt_dataset)
python
EVAL_RUN = True
python
for model_name in ["gpt-4o-2024-08-06"]:
pipeline = CodeGenerationPipeline(model_name=model_name)
if not EVAL_RUN:
dataset = prompt_dataset.rows[2]
result = await pipeline.predict(dataset["prompt"])
score_result = await score_humaneval_test(
dataset["test"], dataset["entry_point"], result["generated_code"].full_code
)
else:
evaluation = Evaluation(
name="minimal_code_gen_evaluation",
dataset=prompt_dataset,
scorers=[score_humaneval_test],
)
results = await evaluation.evaluate(pipeline)
 이 예제에서는 Weave와 OpenAI의 언어 모델을 사용하여 코드 생성 파이프라인을 구현하는 방법을 보여주었습니다. 다음과 같은 방법을 보여주었습니다:
이 예제에서는 Weave와 OpenAI의 언어 모델을 사용하여 코드 생성 파이프라인을 구현하는 방법을 보여주었습니다. 다음과 같은 방법을 보여주었습니다:
- 코드 생성 프로세스의 각 단계에 대한 Weave 작업 생성
- 쉬운 추적 및 평가를 위해 파이프라인을 Weave Model로 래핑
- Weave 작업을 사용하여 사용자 정의 평가 지표 구현
- 데이터셋 생성 및 파이프라인 평가 실행
Weave의 원활한 통합을 통해 코드 생성 프로세스 전반에 걸쳐 입력, 출력 및 중간 단계를 추적할 수 있어 LLM 애플리케이션을 더 쉽게 디버깅, 최적화 및 평가할 수 있습니다.
Weave 및 그 기능에 대한 자세한 정보는 Weave documentation을 확인하세요. 이 예제를 확장하여 더 큰 데이터셋을 처리하거나, 더 정교한 평가 지표를 구현하거나, 다른 LLM 워크플로우와 통합할 수 있습니다.
 이제 핵심 코드 생성 로직을 구현해 보겠습니다:
우리는
이제 핵심 코드 생성 로직을 구현해 보겠습니다:
우리는 


